Considering permanent birth control? The Filshie clip offers a highly effective method, but understanding both its benefits and potential drawbacks is crucial. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the Filshie clip, covering its efficacy, safety, and long-term implications, including its strengths and weaknesses compared to other methods. We aim to address key questions such as: How does it work? What are the potential complications, and how can they be minimized? What are the alternatives?
Understanding the Filshie Clip Mechanism and Surgical Outcomes
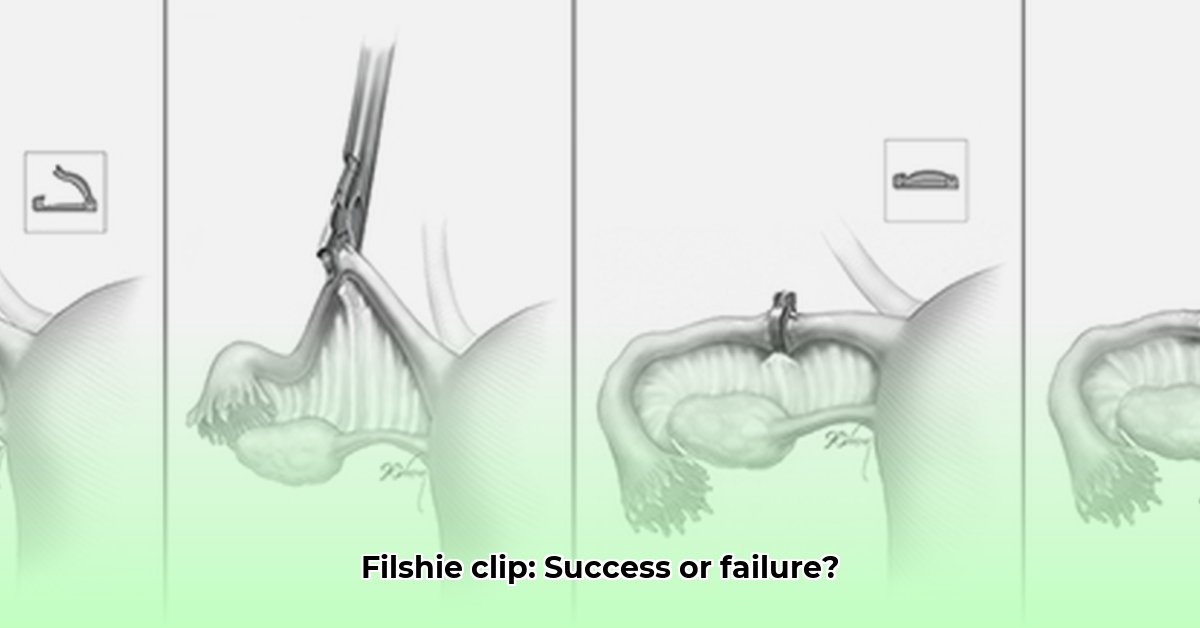
The Filshie clip, a small titanium clamp lined with silicone, presents a popular choice for female sterilization. Applied to the fallopian tubes—utilizing minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery—it blocks the passage of eggs to achieve permanent birth control. This method offers a swift procedure without extensive incisions.
How the Filshie Clip Works: A Precise Blockage
During the procedure, a surgeon carefully positions the Filshie clip onto the fallopian tubes. Its design adapts to accommodate tubes that may be slightly swollen, offering an advantage over alternative methods. The clip compresses the fallopian tube, causing localized tissue death (necrosis) and eventual scarring (fibrosis). This permanently blocks the tube, preventing eggs from traveling from the ovaries to the uterus, effectively preventing pregnancy and ensuring minimal invasiveness.
Success Rates: High Efficacy in Pregnancy Prevention
Studies consistently demonstrate high effectiveness of the Filshie clip in preventing pregnancy.
- Its primary function, stopping fertilization, results in exceptionally low rates of ectopic pregnancies (pregnancies outside the uterus), significantly lower than other tubal occlusion methods. Studies show rates as low as 0.016%.
- Leading medical organizations, such as the UK Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, frequently recommend this sterilization method due to its high success rate and ease of application.
- The Filshie clip’s primary function—stopping fertilization—is something it does extremely well, boasting successful placement rates approaching 100%.
Migration and Expulsion Risks: Acknowledging Potential Complications
Although very effective, the Filshie clip presents small risks of migration (moving from its original position) or expulsion (falling off completely). Awareness of these infrequent yet potential complications is important. Reported migration rates vary across studies, ranging from 0.1% to 0.6% of cases, influenced by surgical techniques, patient characteristics, and tracking methods.
Factors contributing to migration or expulsion involve the body’s response to the clip, variations in surgical technique, and even the timing of the procedure (e.g., postpartum). Understanding these risks aids in informed decision-making.
Potential Complications: Monitoring Post-Procedure
Complications, although uncommon, can occur and require close monitoring.
- Some women report pain or cramping after the procedure, especially during the postpartum period. Chronic abdominal pain has also been reported in rare cases due to clip migration.
- There’s a small chance of infection at the incision site or in the pelvic area. Sterishot II applicators, which are single-use, help to minimize the risk of cross-contamination and infection.
- An ectopic pregnancy remains a possibility, although the risk is very low.
- Symptoms of a migrated clip include persistent abdominal pain, abscesses, or, in extremely rare cases, extrusion of the clip through anatomical sites.
- Regular follow-up is crucial, highlighting the importance of monitoring for varied symptoms.
Comparing Filshie Clips to Other Methods
Hulka Clip Analysis
The Hulka clip, made of plastic with a gold spring lock, provides an alternative to Filshie clips for tubal ligation, with the main difference lying in the design and materials. Hulka clips are shaped differently and tend to cause more tissue adhesion, potentially lowering the risk of migration but possibly increasing the risk of pain. They are less commonly used now than Filshie clips.
Other Tubal Ligation Methods
Other methods include:
- Tubal Ligation with Rings (Yoon Band): A silicone band is placed around a loop of the fallopian tube.
- Electrocoagulation/Cauterization: Using electrical current to burn and seal the fallopian tubes. This method carries a higher risk of ectopic pregnancy if it fails.
- Salpingectomy: Complete removal of the fallopian tubes, increasingly favored due to its potential to reduce the risk of ovarian cancer.
Individual circumstances and healthcare provider guidance should inform the choice between the available methods.
Candidate Selection: Ideal Filshie Clip Candidates
Ideal candidates for Filshie clip sterilization are women certain about not wanting children in the future. Factors such as postpartum or post-abortion status may slightly increase complication risks. Open communication with a doctor is crucial for individual assessments and determining the best path.
Long-Term Effects: Ongoing Research and Considerations
Ongoing research examines the long-term effects of the Filshie clip to identify how it could impact a woman’s overall health. Studies explore potential links to gynecological issues, but current findings aren’t conclusive. More research is needed to understand long-term implications fully. Some studies have explored the possibility of post-tubal ligation syndrome, but this remains a controversial topic.
Actionable Steps: Guidelines for Stakeholders
| Stakeholder | Short-Term Actions | Long-Term Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Surgeons/Gynecologists | Utilize optimal surgical techniques, including careful clip placement and gentle tissue handling; carefully select patients, considering individual risk factors; provide thorough pre-operative counseling about the risks and benefits of the procedure. | Participate in training programs and research, refine best practices, and adopt Sterishot II technology (single-use applicator); advocate for standardized reporting of complications and long-term outcomes. |
| Patients | Seek detailed information from trusted sources; understand the procedure, risks, and alternatives; ensure thorough informed consent, and discuss all concerns with surgeons; maintain realistic expectations about the procedure and its potential effects. | Attend all follow-up appointments and be aware of potential post-operative symptoms; report any unusual pain or discomfort to your healthcare provider promptly; ensure ongoing support and access to reliable information. |
| Regulatory Bodies | Continuously update guidelines based on emerging research and adverse event reports; monitor device performance and safety through post-market surveillance; ensure transparent communication of risks and benefits to both healthcare providers and patients. | Secure funding for research on long-term effects, including potential links to gynecological issues; improve data collection and analysis; establish standardized reporting methods for complications. |
| Device Manufacturers | Focus on the development of safer and more reversible sterilization technology; conduct rigorous testing of device performance and biocompatibility; provide comprehensive training and support to surgeons using the Filshie clip system. | Design improvements to minimize migration risk; explore the use of advanced materials to improve biocompatibility and reduce complications; support independent research on the long-term effects of the device. |
Note: This review serves only educational purposes for Filshie clip sterilization. Always consult with qualified healthcare professionals for personalized medical advice.
How to Minimize Filshie Clip Migration Risk During Sterilization
Filshie clip migration, while uncommon, can lead to serious complications. Understanding the risks and benefits promotes informed consent.
Key Takeaways:
- Filshie clip migration, while uncommon, can lead to serious complications.
- Careful surgical technique is paramount in preventing migration.
- Patient selection and post-operative monitoring play crucial roles.
- Understanding the risks and benefits is vital for informed consent.
Understanding the Filshie Clip
The Filshie clip is a small titanium device used for female sterilization. It’s applied to the fallopian tubes to block the passage of eggs. While highly effective, like any medical procedure, it carries risks. One potential complication is clip migration, where the clip moves from its original placement.
Why Does Migration Happen?
The precise reasons for Filshie clip migration remain unclear. Some theories suggest inflammation weakens the surrounding tissue, allowing the clip to shift. Incomplete occlusion of the tube, improper clip placement, and individual anatomical variations may also contribute. Gravity might also contribute to the displacement of the clip over time.
How Common is Clip Migration?
Studies estimate Filshie clip migration occurs in only 0.1% to 0.6% of cases. However, some lawsuits suggest the rate may be higher. That’s a small percentage, but the potential consequences make understanding and minimizing this risk vital.
What are the Consequences of Migration?
Clip migration can cause problems. The most common complication is pain, either acute or chronic abdominal pain. In more severe cases, bowel obstruction or infection can occur, necessitating surgery. Migrated clips can also embed themselves in other organs, leading to further complications.
How to Minimize Filshie Clip Migration Risk During Sterilization: A Multifaceted Approach
Minimizing the risk of Filshie clip migration involves collaboration between the surgeon and the patient. The focus remains on meticulous technique and careful patient selection.
For Surgeons:
- Precise Placement: Ensure the clip is securely attached to the fallopian tube, avoiding excessive tissue trauma. The clip should be placed perpendicular to the tube to ensure complete occlusion.
- Appropriate Tissue Handling: Gentle manipulation of tissues minimizes inflammation and the chances of displacement. Avoid excessive traction or stretching of the fallopian tube
- Stainless Food Storage Keeps Your Kitchen Organized And Meals Fresh - February 28, 2026
- Stainless Steel Food Storage for Healthier, Eco-Friendly Meal Prep - February 27, 2026
- Stainless Food Containers Offer Durable Storage for Everyday Meals - February 26, 2026