Living with HIV presents unique financial challenges. This guide provides a roadmap to navigating the costs of HIV treatment in 2024, offering practical advice and resources to help you access affordable, quality care.
Decoding HIV Treatment Expenses
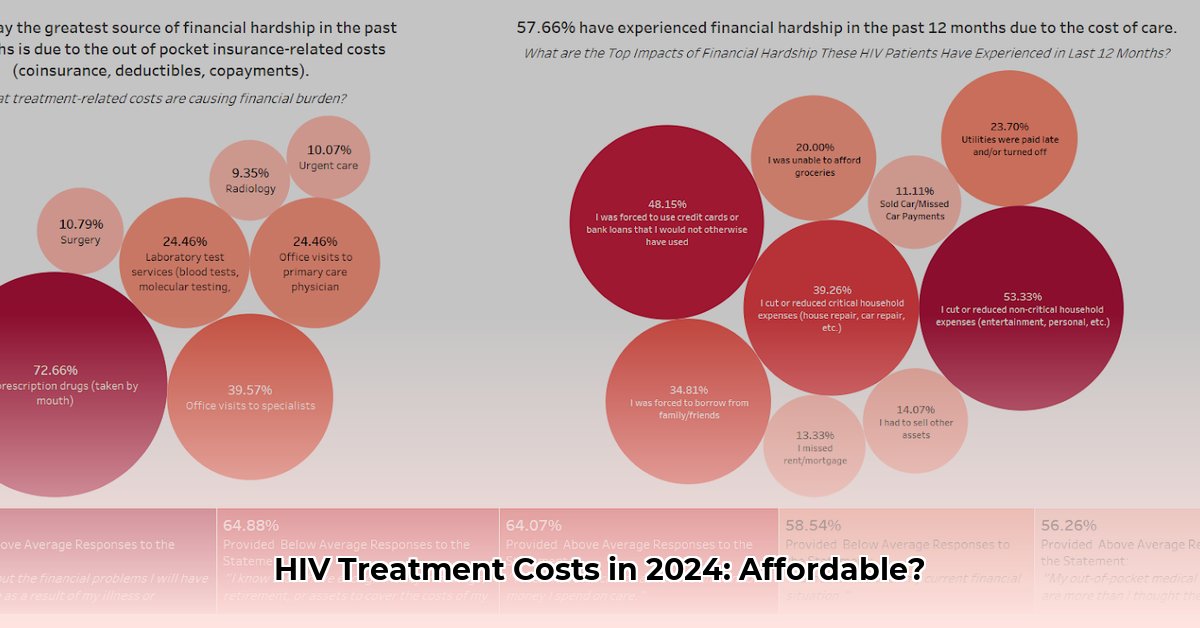
Understanding the factors that influence HIV treatment costs is the first step towards managing them effectively. It’s a complex landscape, but we’ll break it down into manageable pieces.
Medication Type: Brand Name vs. Generic
One of the biggest cost drivers is medication. Brand-name drugs are typically much more expensive than their generic counterparts. Generics contain the same active ingredients and are generally as effective. Discuss with your doctor whether switching to a generic version is appropriate for your specific situation.
Insurance Coverage: Navigating Your Plan
Health insurance, including Medicare and Medicaid, can significantly lower your out-of-pocket expenses. However, even with insurance, you’ll likely encounter costs like co-pays, deductibles, and premiums. Understanding your plan’s specifics is crucial. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) prevents insurers from denying coverage based on HIV status. If navigating your insurance plan feels overwhelming, resources are available to help you understand your options ([link to a resource explaining insurance terms and coverage]).
Healthcare Provider and Location: Geographic Variations
Where you live and receive care can surprisingly impact costs. Healthcare expenses, like housing costs, vary geographically. Doctor visit fees, lab test prices, and even medication costs can fluctuate based on location. Researching providers and comparing prices in different areas can sometimes reveal more affordable options ([link to a tool or resource if one exists that allows comparison by location]).
Additional Medical Needs: A Holistic Approach
Managing other health conditions alongside HIV can add to the overall cost of your care. More frequent doctor visits, specialist consultations, and additional medications all contribute to expenses. It’s vital to be open with your healthcare team about all your health needs so they can help coordinate care efficiently and explore potential cost savings.
Breaking Down Typical Expenses
A clear understanding of where your money is going empowers you to make informed decisions. Here’s a breakdown of common HIV treatment expenses:
-
Medication Costs: This is often the most significant expense. Brand-name ART can range from $1,700 to over $9,000 per month. Generic versions are typically much more affordable, ranging from $110 to $1,200 monthly.
-
Doctor Visits and Specialist Fees: Regular checkups with your HIV specialist are essential. The cost of these visits varies depending on your provider and insurance coverage.
-
Laboratory Testing: Monitoring your viral load and CD4 count requires routine blood tests, which add to the overall cost.
-
Other Related Expenses: Factor in costs like transportation to appointments, over-the-counter medications for side effects, and potentially nutritional supplements.
Actionable Strategies for Reducing Costs
Don’t let cost concerns prevent you from getting the care you need. Here are proactive steps you can take:
-
Choose Generic Medications: When possible, opting for generics can significantly reduce medication expenses. Discuss this option with your doctor.
-
Utilize Patient Assistance Programs (PAPs): Many pharmaceutical companies offer PAPs to help cover medication costs for eligible individuals. Contact the pharmaceutical company directly or ask your doctor for information ([link to a general resource on PAPs or a directory]).
-
Access AIDS Drug Assistance Programs (ADAPs): ADAPs are state-run programs offering financial support for HIV-related medications and services. Eligibility criteria vary by state ([link to the national ADAP directory]).
-
Negotiate with Your Insurance Company: Don’t hesitate to discuss payment options or potential discounts with your insurance provider.
-
Maximize Insurance Benefits: Understand your plan’s details to ensure you’re utilizing all available benefits, such as wellness programs or prescription discounts.
-
Develop a Realistic Budget: Track your expenses and create a budget to gain control of your finances and identify potential savings.
Finding Support and Resources
You are not alone in this journey. Several resources offer valuable assistance:
-
Support Groups: Connect with others facing similar challenges ([link to relevant support group resources]).
-
Financial Advisors: A financial advisor can help you create a long-term financial plan, incorporating your healthcare expenses (consider advisors specializing in long-term care planning).
-
Mental Health Professionals: Managing the emotional and psychological aspects of living with HIV is important. Don’t hesitate to seek professional support ([link to mental health resources]).
-
Your Healthcare Team: Open communication with your doctor, nurse, or social worker is crucial. They can provide guidance on treatment options, cost-saving strategies, and connect you with relevant resources. They can also help address any anxieties you may have about discussing financial concerns.
Long-Term Financial Planning with HIV
Living with HIV requires ongoing financial planning. Consider these key aspects:
-
Understanding Long-Term Costs: Projecting future expenses for medications, doctor visits, and potential hospitalizations can help you prepare financially.
-
Planning for Retirement: Consult a financial advisor specializing in retirement planning for individuals with chronic illnesses like HIV.
-
Insurance and Financial Assistance: Stay informed about changes in your insurance coverage and explore all available financial assistance programs. The table below summarizes key differences between Patient Assistance Programs (PAPs) and AIDS Drug Assistance Programs (ADAPs):
| Feature | PAP | ADAP |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility | Based on income and insurance status; varies by drug manufacturer | Based on income and resources; varies by state |
| Coverage | Usually covers specific medications | Can cover a wider range of HIV-related services |
| Application | Apply directly to the drug manufacturer | Apply through your state’s ADAP program |
- Legal and Estate Planning: Consider creating a living will, establishing a power of attorney, and developing an estate plan to ensure your wishes are respected.
Staying Informed
HIV treatment and related costs can change. Staying updated is essential. Consult reputable sources like the CDC (cdc.gov) and the NIH (nih.gov) for the latest information.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical or financial advice. Consult with your healthcare providers and financial advisors for personalized guidance.
- Food Making Kits Bring Easy, Fun Homemade Dishes to Your Kitchen - February 5, 2026
- Cooking Kits Make Mastering New Recipes Fun for Everyone - February 4, 2026
- Leak-Proof Glass Food Containers with Locking Lids Keep Food Fresh - February 3, 2026