Experiencing a sudden dark spot or tenderness in your gums can be alarming. This comprehensive guide explores the world of bruised gums, providing you with the knowledge to identify, treat, and prevent this common oral health issue. From everyday mishaps to underlying health concerns, we’ll cover the various causes, symptoms, and treatment options, empowering you to maintain a healthy, vibrant smile.
Decoding the Mystery of Bruised Gums
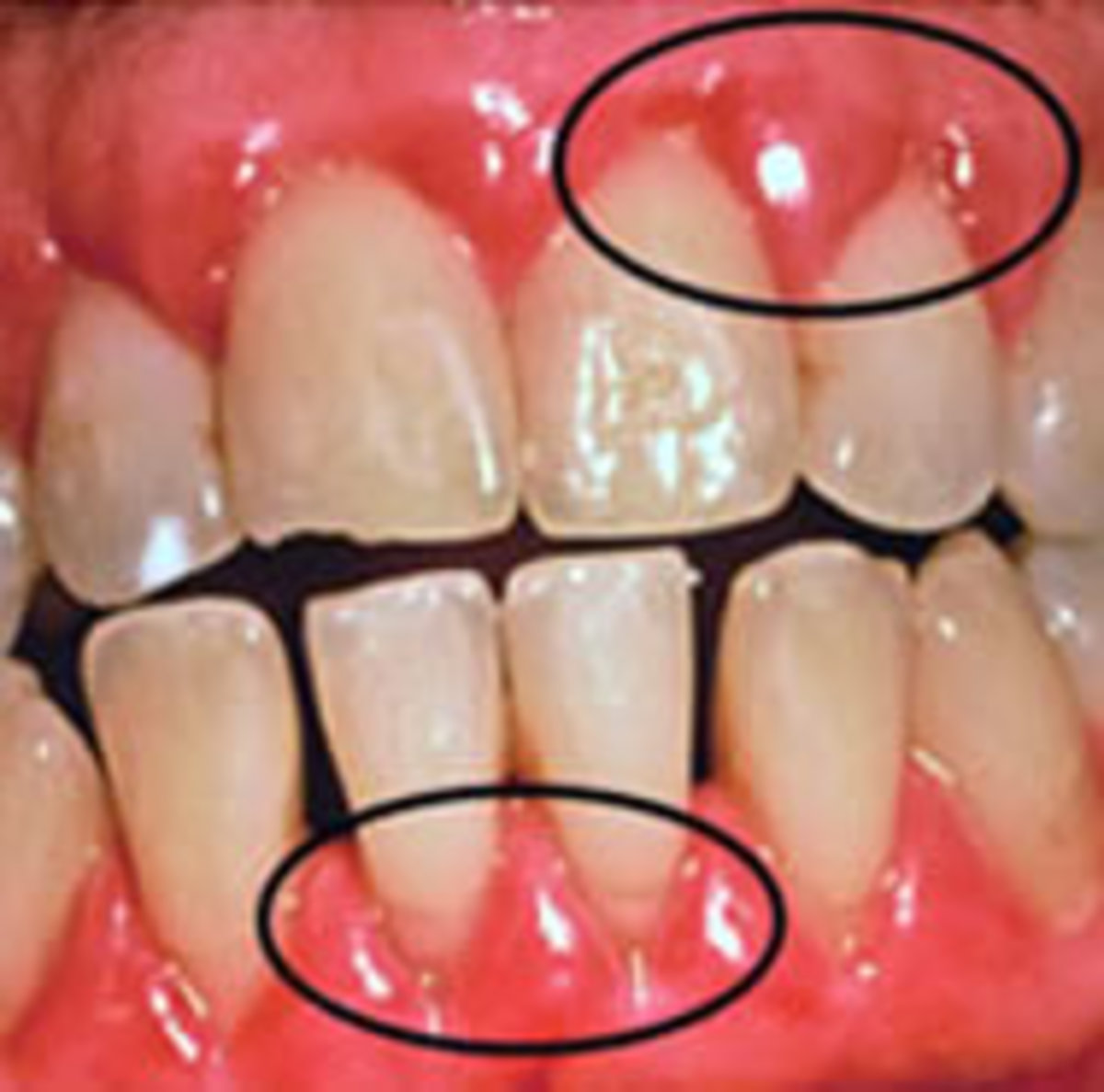
A bruised gum, also known as a gingival hematoma, occurs when the soft tissues of your gums experience trauma, leading to pain, swelling, and discoloration. While often harmless and self-resolving, understanding the underlying causes is crucial for effective treatment and prevention.
What Causes Bruising in the Gums?
Gum bruising can stem from a variety of sources, ranging from simple everyday occurrences to more complex medical conditions.
Physical Trauma: This is the most common cause, often resulting from:
- Aggressive Brushing/Flossing: Overly vigorous brushing or incorrect flossing technique can irritate and bruise delicate gum tissue.
- Accidental Injury: Biting down on hard foods (like popcorn kernels or ice), a fall, sports injuries, or even dental procedures can cause gum trauma.
- Ill-fitting Dentures/Appliances: Dentures that don’t fit properly or orthodontic appliances can rub against the gums, leading to chronic irritation and bruising.
- Oral Piercings: Tongue or lip piercings can also traumatize gum tissue, increasing the risk of bruising.
Infections: Infections in the mouth can weaken gum tissue and make it more susceptible to bruising. These include:
- Gingivitis: Inflammation of the gums, often caused by plaque buildup, can make gums tender, red, and prone to bleeding and bruising. Read more about gingivitis.
- Periodontitis: A more severe form of gum disease that can damage the soft tissues and bone supporting the teeth, increasing the risk of bruising and other complications. Learn about periodontitis.
- Abscesses: Pockets of pus that form in the gums or around the teeth can cause pain, swelling, and discoloration, potentially resembling a bruise.
Medical Conditions: Certain underlying health conditions can affect gum health and increase the likelihood of bruising.
- Thrombocytopenia (Low Platelet Count): Platelets are essential for blood clotting, so a low count can increase bleeding and bruising throughout the body, including the gums.
- Vitamin Deficiencies (e.g., Vitamin C): While less common in developed countries, vitamin C deficiency can weaken blood vessels and contribute to gum bleeding and bruising. Discover the importance of vitamins.
Other Contributing Factors:
- Certain Medications: Blood thinners and some other medications can increase the risk of bleeding and bruising.
- Hormonal Changes (e.g., Pregnancy, Menopause): Hormonal fluctuations can make gums more sensitive and prone to bleeding.
- Stress: Chronic stress can increase inflammation throughout the body, potentially exacerbating gum problems and making them more susceptible to bruising. Explore the link between stress and health.
Recognizing the Signs: Symptoms of Bruised Gums
Identifying a bruised gum is usually straightforward. Look for these common symptoms:
- Discoloration: Gums might appear darker than usual, ranging from red and purple to brown or even black.
- Swelling: The affected area may be noticeably swollen and puffy.
- Tenderness/Pain: The bruised area will likely be tender or painful to the touch, especially when eating, brushing, or flossing.
- Bleeding: While not always present, bleeding, especially after brushing or flossing, can be a sign of bruised gums, particularly if accompanied by other symptoms.
Soothing the Soreness: Treatment for Bruised Gums
Most bruised gums heal naturally within a few days to a couple of weeks, similar to a minor skin bruise. However, several home remedies can help soothe discomfort and promote healing:
- Saltwater Rinses: Dissolve 1 teaspoon of salt in 1 cup of warm water and rinse gently for 30 seconds, several times a day. This helps cleanse the area and reduce inflammation.
- Cold Compress: Apply a cold pack wrapped in a thin cloth to the outside of your cheek near the bruised area for 10-15 minutes at a time. This can help numb the pain and reduce swelling.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and discomfort. Always follow the recommended dosage.
For persistent pain, excessive bleeding, signs of infection (pus, fever), or if the discoloration doesn’t improve, consult your dentist. They can diagnose the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment. This may include:
- Scaling and Root Planing (for gum disease): A deep cleaning procedure to remove plaque and tartar from below the gum line.
- Antibiotics (for infection): To eliminate bacterial infections.
- Gum Surgery (in rare, severe cases): For extensive gum damage.
Are you in need of transporting blood? Get the best deals on our high-quality bag for blood.
Preventing Bruised Gums: Proactive Steps for a Healthy Smile
Taking proactive steps can significantly reduce your risk of bruising your gums:
- Gentle Brushing/Flossing: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle, circular motions. Master proper flossing techniques to avoid snapping the floss against your gums. Learn proper brushing techniques.
- Balanced Diet: A nutritious diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially vitamin C, supports healthy gum tissue. Explore foods for healthy gums.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Regular dental visits allow your dentist to identify and address potential issues early on, including gum disease, before they lead to complications like bruising.
- Protective Mouthguards: If you play sports, wear a mouthguard to protect your gums and teeth from impact.
- Managing Underlying Medical Conditions: If you have a condition that increases your risk of bleeding or bruising, work closely with your physician to manage it effectively.
Beyond the Bruise: Long-Term Gum Health
While a single bruised gum is usually not a cause for concern, recurring bruising or persistent symptoms warrant a visit to your dentist. They can determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment. Remember, healthy gums are essential for a healthy smile, and understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for bruised gums empowers you to take control of your oral health.
- Food Making Kits Bring Easy, Fun Homemade Dishes to Your Kitchen - February 5, 2026
- Cooking Kits Make Mastering New Recipes Fun for Everyone - February 4, 2026
- Leak-Proof Glass Food Containers with Locking Lids Keep Food Fresh - February 3, 2026