Blood bags are more than just storage containers; they are sophisticated systems vital for safe blood collection, component separation, and transfusion. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of blood bag technology, from the materials used in their construction to the latest innovations shaping the future of blood storage. Whether you’re a seasoned healthcare professional or simply curious about this critical aspect of modern medicine, this guide will provide valuable insights into the world of blood bags.
Understanding Blood Bag Basics
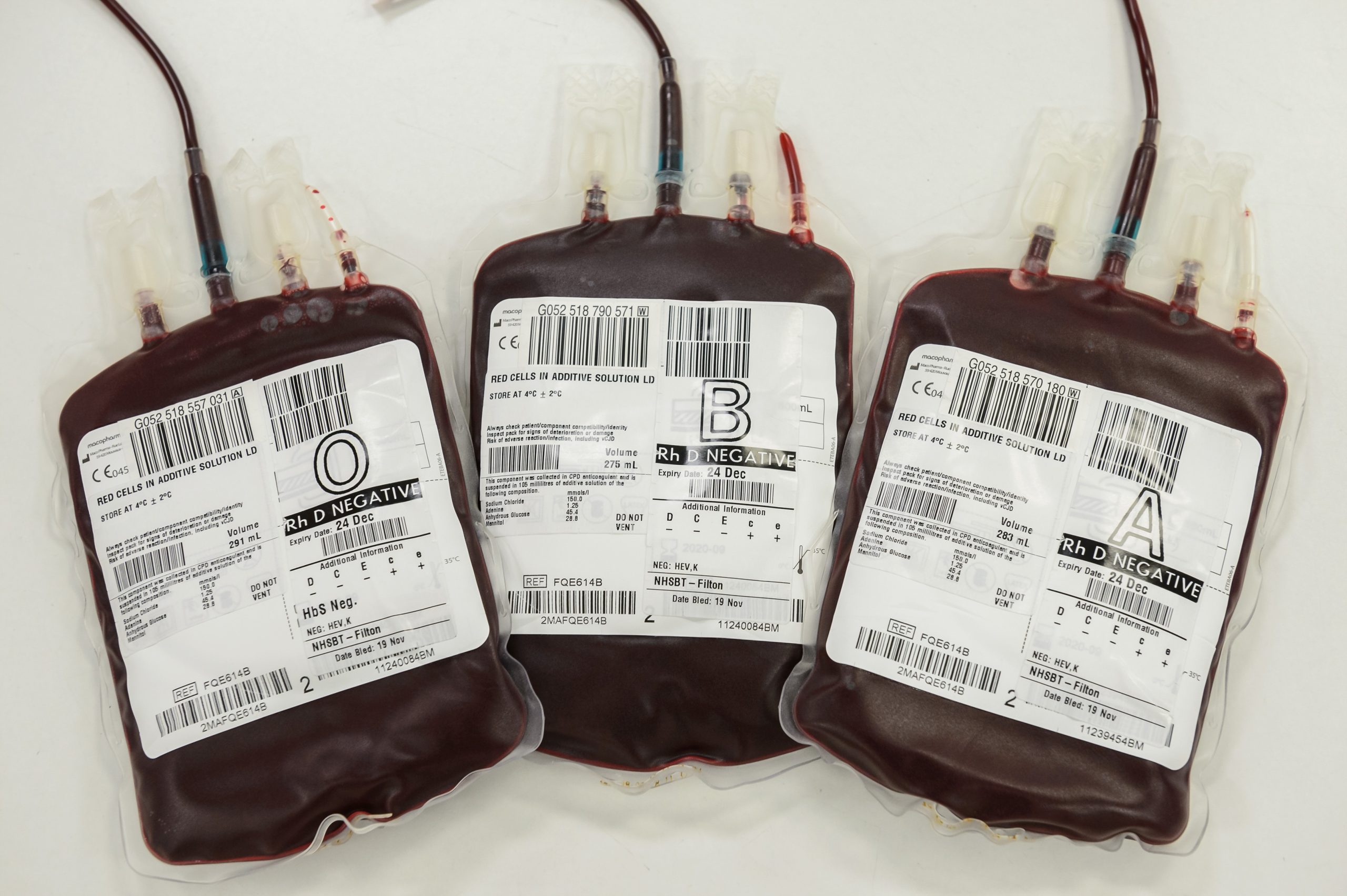
Blood bags are sterile, single-use containers designed for the collection, storage, and transfusion of blood and its components. These specialized bags play a crucial role in blood banks, hospitals, and any medical setting where blood transfusions are performed. Their importance lies in maintaining the safety and efficacy of blood products, ultimately contributing to positive patient outcomes. Let’s explore the essential components of a typical blood bag system:
- Primary Bag: This main pouch serves as the initial reservoir for collected blood. Its flexible, medical-grade plastic construction (often PVC or non-PVC alternatives like EVA) ensures sterility and helps prevent contamination.
- Satellite Bags: Attached to the primary bag, these smaller compartments enable the separation and storage of specific blood components like red blood cells, plasma, and platelets. This separation is crucial for tailoring transfusions to individual patient needs. If your gums are swollen, bleeding, or bruised gums, it’s important to see a dentist as soon as possible. This seemingly unrelated point highlights the interconnectedness of medical procedures and the importance of blood transfusions in various health situations.
- Tubing and Needles: Specialized tubing connects the donor’s vein to the primary bag, facilitating efficient blood collection. Needles, an integral part of the system, are designed for safe and comfortable insertion.
- Anticoagulant Solutions: To prevent clotting and preserve the viability of the collected blood, anticoagulant solutions like CPD or CPDA-1 are incorporated into the bag’s design. The specific anticoagulant used may vary depending on the intended use of the blood product.
Exploring the Diverse Types of Blood Bags
From single to quadruple chambers, blood bags are tailored to specific needs, ensuring optimal preservation and utilization of precious blood components. The choice of blood bag depends largely on the intended application:
- Single Bags: These bags are the simplest type, utilized for collecting whole blood, where all components remain unseparated.
- Double Bags: Designed with two compartments, these bags allow for the separation of red blood cells from plasma.
- Triple Bags: With three compartments, these bags enable the separation of red blood cells, plasma, and platelets.
- Quadruple Bags: The most complex type, quadruple bags, facilitate the separation of red blood cells, plasma, platelets, and cryoprecipitate, a clotting factor crucial for certain medical conditions.
Key Considerations for Blood Bag Selection
Navigating the market for blood bags requires understanding various factors, including material, volume, anticoagulant solutions, and compatibility with blood bank equipment. Selecting the right blood bag is a critical step in ensuring transfusion safety and efficacy:
- Volume Capacity: Blood bags come in a variety of sizes, ranging from 100ml to 600ml and larger, to accommodate different transfusion requirements. The volume needed is determined by the specific clinical situation.
- Material: While PVC has been the traditional material, non-PVC options like EVA are gaining popularity due to their increased flexibility and potentially reduced environmental impact. The choice of material may also affect the storage duration of the blood product.
- Anticoagulant Solution: Different anticoagulants have varying effects on blood components and storage duration. The selection of the appropriate anticoagulant is crucial for maintaining blood quality and preventing adverse reactions.
- Compatibility with Blood Bank Equipment: Ensuring compatibility between the blood bag and blood bank equipment, such as centrifuges and storage systems, is paramount for efficient processing and storage.
Leading Manufacturers and Market Overview
Several companies specialize in the production of blood bags, contributing to the ongoing advancements in this field. Key players include:
- Terumo BCT: Known for its innovative blood collection and processing systems.
- Fresenius Kabi: A global healthcare company providing a wide range of medical products, including blood bags.
- Grifols: Specializing in plasma-derived therapies and transfusion medicine products.
- Macopharma: Offers a range of blood bags and related products for transfusion medicine.
Prices for blood bags can vary considerably, ranging from approximately $14 for simpler bags to over $1800 for specialized systems with advanced features. Suppliers such as Grayline Medical, Serfinity Medical, StomaBags.com, and DripArmor.com offer a variety of blood bag options to meet diverse needs.
The Future of Blood Storage: Innovations and Challenges
Advancements in blood bag technology are revolutionizing blood banking, enhancing safety, prolonging storage durations, and improving patient outcomes. Ongoing research and development efforts focus on several key areas:
- Improved Materials: Scientists are exploring new polymers and coatings that offer enhanced biocompatibility, reduced risk of storage lesions, and potentially longer shelf life for blood products.
- Advanced Anticoagulant Solutions: Research continues to refine anticoagulant solutions to optimize blood component preservation and minimize the risk of adverse reactions during transfusions.
- Smart Blood Bags: The integration of sensors and tracking technology into blood bags may one day allow for real-time monitoring of blood quality, temperature, and other critical parameters, enhancing safety and traceability.
However, challenges remain, including environmental concerns associated with traditional PVC blood bags and the ongoing need to address blood shortages. The development of more sustainable materials and innovative preservation techniques offers promising avenues for future advancements.
Conclusion
Blood bags are much more than simple containers; they are integral components of modern medicine, ensuring the safe and effective delivery of life-saving blood transfusions. Ongoing research and development efforts promise to further enhance the safety, efficacy, and sustainability of blood bag technology, ultimately improving patient care and addressing global health challenges.