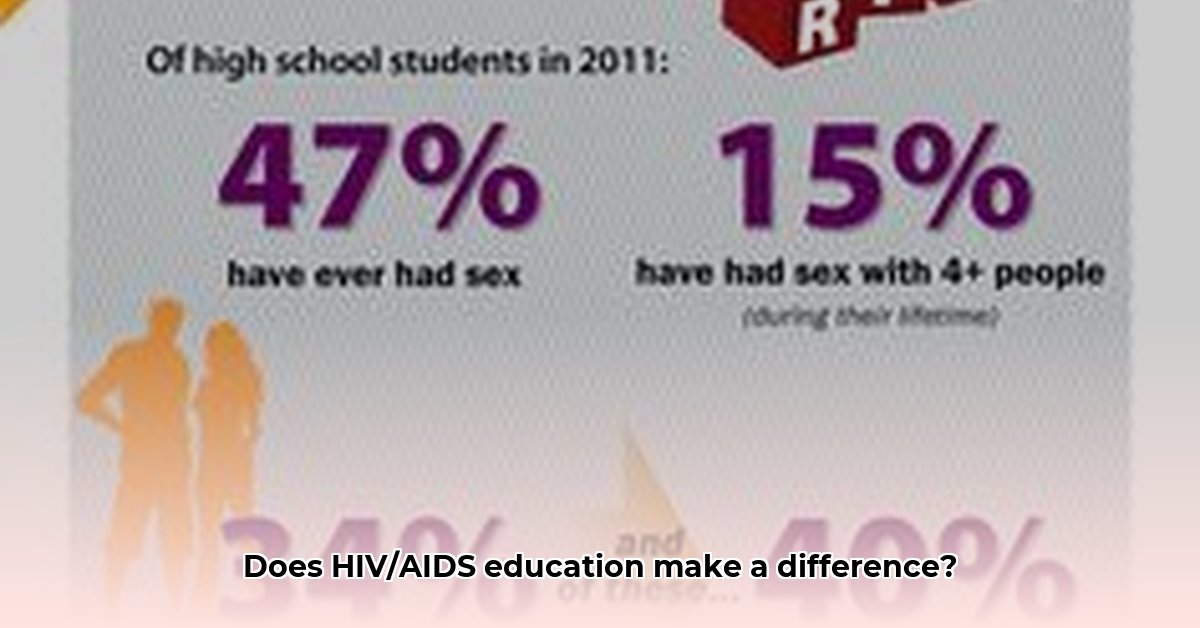
HIV/AIDS education remains a cornerstone in the global fight against the epidemic. This report analyzes the statistical impact of education on HIV/AIDS prevention, testing, treatment adherence, and public perception. We’ll explore data-driven insights, visualize key trends, and discuss the implications for future strategies.
Global HIV/AIDS Statistics: Understanding the Current Landscape
The global fight against HIV/AIDS presents a complex picture. Millions live with the virus, underscoring the need for continued education and prevention. UNAIDS data reveals the following:
- People living with HIV (2022): [Insert 2022 data from UNAIDS]
- New HIV Infections (2022): [Insert 2022 data from UNAIDS]
- AIDS-Related Deaths (2022): [Insert 2022 data from UNAIDS]
- Access to Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) (2022): [Insert 2022 data from UNAIDS]
(Include a chart visualizing these global statistics)
These figures highlight the persistent global challenge and the need for sustained, impactful interventions.
HIV/AIDS in the US: A Closer Examination
The CDC provides a detailed view of the epidemic within the United States:
- New HIV Diagnoses (Latest Year): [Insert latest data from CDC]
- People living with HIV (Latest Year): [Insert latest data from CDC]
- Deaths (Latest Year): [Insert latest data from CDC]
(Include a chart or map visualizing US statistics, potentially showing regional variations)
Further analysis reveals disparities across demographics, emphasizing the need for tailored educational programs. For instance, certain racial and ethnic groups, men who have sex with men, and individuals in specific geographic locations experience higher rates of HIV.
The Power of Education: Driving Positive Change
While quantifying the precise impact of education on HIV/AIDS outcomes is complex, studies suggest strong correlations between educational interventions and positive changes in several key areas:
Increased HIV Testing Rates
Education empowers individuals to take control of their health by promoting HIV testing. Increased awareness of testing availability, coupled with reduced stigma surrounding HIV, likely contributes to higher testing rates.
Improved Treatment Adherence
Adherence to antiretroviral therapy (ART) is crucial for managing HIV. Education equips individuals with the knowledge and support they need to adhere to their treatment plans, leading to improved health outcomes and reduced transmission rates.
Behavior Modification
Education plays a role in promoting safer sexual practices, such as consistent condom use and reduced numbers of sexual partners. While long-term behavior change is challenging, educational programs contribute to increased awareness of risk factors and promote healthier choices.
Shifting Public Perceptions
Education combats misinformation and stigma surrounding HIV/AIDS. Increased knowledge fosters empathy and understanding, creating a more supportive environment for those living with the virus.
Exploring Educational Approaches: A Multifaceted Strategy
Effective HIV/AIDS education encompasses a range of approaches:
Peer Education
Peer-led programs leverage the power of shared experience and relatable role models. Research suggests these programs can reduce HIV infection rates by up to 36%, particularly among high-risk groups. They also demonstrably increase HIV testing and condom use.
School-Based Education
Comprehensive, age-appropriate sex education in schools is fundamental. These programs improve knowledge about HIV/AIDS and promote safer sexual practices among young people, particularly in resource-limited settings.
Technological Advancements
Emerging technologies, such as mobile apps and online platforms, offer innovative and cost-effective ways to deliver HIV/AIDS education. Ongoing research explores their long-term effectiveness and potential to reach wider audiences.
Addressing Challenges and Future Directions
Several challenges remain in maximizing the impact of HIV/AIDS education:
Measuring Long-Term Impact
Assessing the long-term effects of educational interventions is complex. Ongoing research seeks to better understand how education translates into sustained behavior change and reduced transmission rates.
Tailoring to Specific Needs
Effective programs tailor their approach to specific communities, considering cultural contexts and individual needs. A one-size-fits-all approach is unlikely to be effective.
Integrating with Other Strategies
Education is most impactful when integrated with other prevention and treatment strategies, such as accessible testing, affordable treatment, and comprehensive support services.
Combating Stigma
Despite progress, stigma remains a significant barrier to HIV prevention and care. Continued efforts to combat stigma and discrimination are essential for maximizing the effectiveness of educational programs.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Importance of HIV/AIDS Education
HIV/AIDS education, though complex and multifaceted, remains a crucial tool in the fight against the epidemic. By understanding the statistical impact of education, tailoring programs to specific needs, and integrating education with other strategies, we can continue to make progress towards a future free from HIV/AIDS. Ongoing research, data analysis, and a commitment to addressing the challenges will be essential for maximizing the effectiveness of HIV/AIDS education in the years to come.
- Delicious Meal Prep Cold Meals Ready to Grab and Go - March 10, 2026
- Cold Meal Prep Makes Healthy, Stress-Free Lunches Easy - March 9, 2026
- Meal Prep Ideas for Healthy Eating Throughout Your Busy Week - March 8, 2026