Experiencing intermittent sharp, stabbing pain in your knee can be concerning. This article provides a comprehensive overview of potential causes, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options for this type of knee pain. Understanding the underlying mechanisms and seeking appropriate medical care are crucial for effective management and prevention of future episodes.
Decoding Intermittent Stabbing Knee Pain
Sudden jabs of pain in your knee can be alarming and disruptive. This intermittent stabbing sensation can stem from a variety of issues, ranging from minor injuries to chronic conditions. Determining the root cause is the first step toward finding relief.
What Could Be Causing the Pain?
Several factors can contribute to sharp, stabbing knee pain that comes and goes. These include:
- Osteoarthritis: This degenerative joint disease involves the gradual breakdown of cartilage, leading to bone-on-bone friction. This can cause sharp pain, particularly during activity. Read more about shoulder bone spurs.
- Cartilage Tears: Tears in the menisci (C-shaped cartilage cushions) can occur due to sudden twisting motions or wear and tear. These tears can cause sharp pain, catching sensations, and limited range of motion.
- Ligament Injuries: Sprains or tears in the ligaments that stabilize the knee joint can result in sharp pain, instability, and difficulty bearing weight.
- Bone Spurs (Osteophytes): Bony growths that develop around the edges of bones can cause sharp pain when they rub against other tissues or restrict movement.
- Baker’s Cysts: Fluid-filled sacs behind the knee can cause a dull ache accompanied by occasional sharp pains, especially when bending the knee.
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome: This condition involves pain around the kneecap, often due to overuse or improper tracking of the kneecap. Sharp, stabbing sensations may occur, especially during activities like running or climbing stairs.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons that connect muscles to bones can cause sharp, burning pain, particularly with movement.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae (fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee joint) can cause sharp, localized pain that worsens with pressure or movement.
- Nerve Issues: Pinched nerves or nerve damage (neuropathy) can cause sharp, shooting pains down the leg that may be felt in the knee.
- Referred Pain: Sometimes, pain originating in other areas, such as the lower back or hip, can radiate to the knee, causing sharp, stabbing sensations.
Diagnosing the Problem
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Your doctor will likely:
- Discuss Your Symptoms: They’ll inquire about the nature of your pain, when it started, what triggers it, and any other accompanying symptoms.
- Perform a Physical Exam: They’ll assess your knee’s range of motion, stability, and points of tenderness. They may also check for swelling, warmth, and any signs of injury.
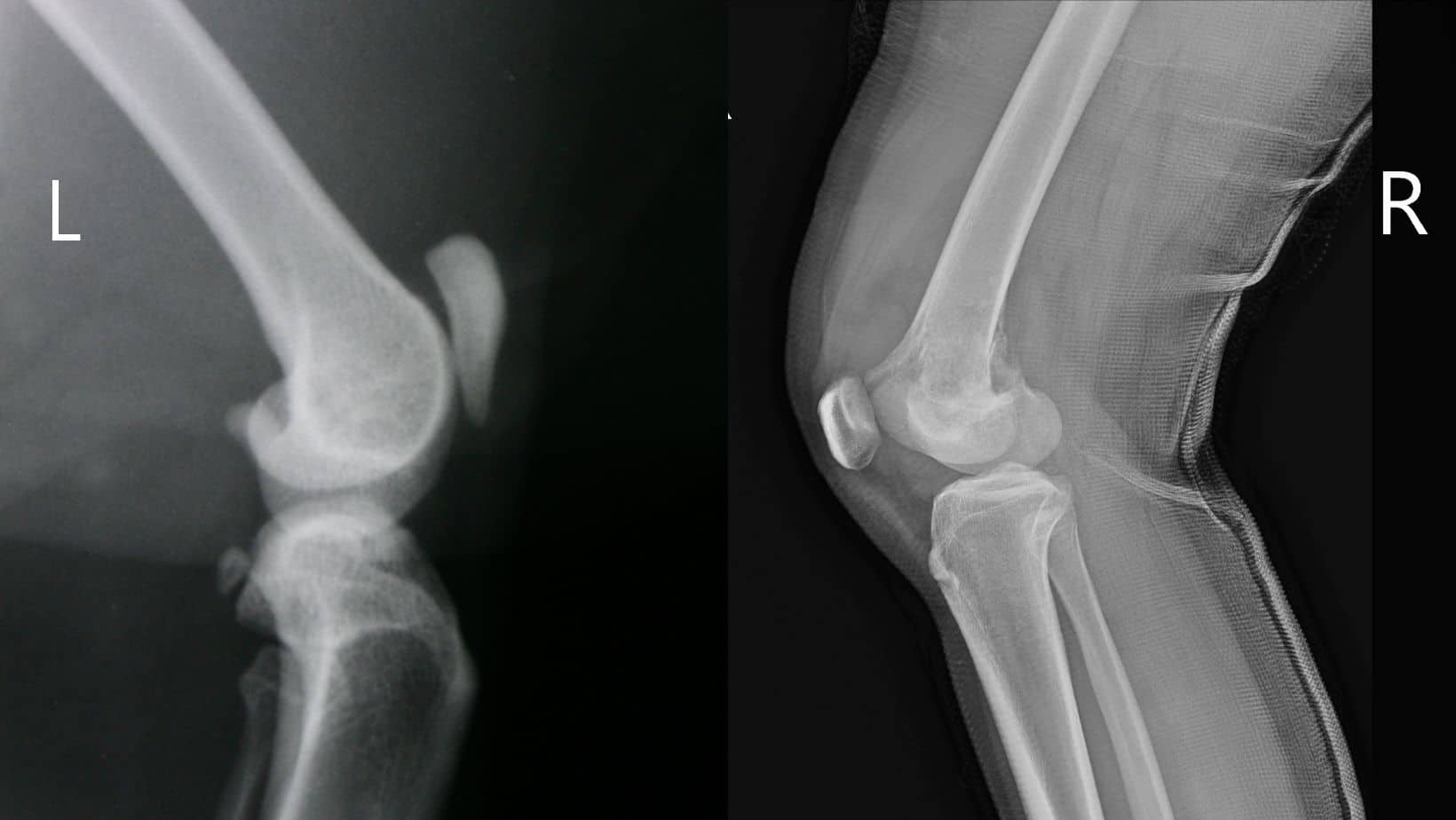
- Order Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans can help visualize the internal structures of your knee and identify any underlying issues, such as fractures, cartilage tears, ligament damage, or bone spurs.
- Analyze Joint Fluid (if present): This can help determine if infection or inflammation is present.
Treatment Options
Treatment for sharp stabbing knee pain depends on the underlying cause and may include:
- Self-Care: Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) can help reduce pain and swelling. Over-the-counter pain relievers may also provide relief.
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises can strengthen supporting muscles, improve flexibility, and restore normal movement patterns.
- Medications: Your doctor may prescribe stronger pain relievers or anti-inflammatory medications if necessary.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief. Viscosupplementation injections can help lubricate the joint.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair damaged tissues, remove bone spurs, or address other structural problems.
Prevention and Long-Term Management
While not all causes of sharp knee pain are preventable, certain strategies can help reduce your risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts added stress on knee joints.
- Strengthen Supporting Muscles: Regular exercise, focusing on strengthening the muscles around your knee, can provide stability and support.
- Choose Appropriate Footwear: Wear supportive shoes with good arch support.
- Warm-up and Cool-down: Always warm up before exercise and cool down afterward to prepare your muscles and prevent injury.
- Use Proper Technique: Pay attention to your form during physical activities to avoid putting undue stress on your knees.
The Importance of Seeking Medical Advice
It’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional if you experience persistent or worsening sharp, stabbing pain in your knee. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help prevent further damage and improve your long-term outcome. Ongoing research continues to explore new and innovative treatment approaches, so there’s always hope for finding even better solutions in the future. Don’t hesitate to discuss your concerns with your doctor and actively participate in your care.
- Food Making Kits Bring Easy, Fun Homemade Dishes to Your Kitchen - February 5, 2026
- Cooking Kits Make Mastering New Recipes Fun for Everyone - February 4, 2026
- Leak-Proof Glass Food Containers with Locking Lids Keep Food Fresh - February 3, 2026