Can You Catch Gum Disease? Separating Fact from Fiction
Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, is a prevalent oral health issue that can lead to tooth loss and other health complications. A common question surrounding this condition is its contagiousness. The answer, like many things in health, isn’t a simple yes or no. While you won’t catch gum disease like a cold, the bacteria that cause it can be transmitted through saliva. This means understanding how these bacteria spread and the factors that influence disease development is crucial for protecting your oral health.
How Periodontal Disease Spreads: Understanding the Risks
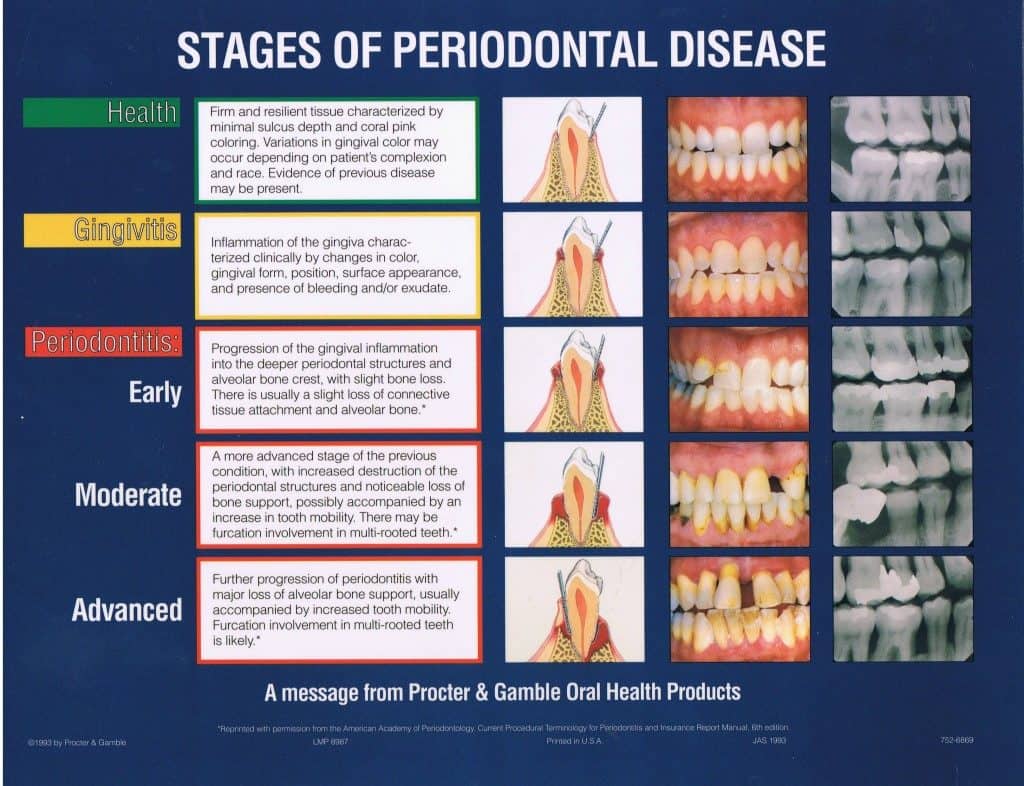
Periodontal disease is an infection affecting the gums and bone that support your teeth. It’s primarily caused by bacteria found in plaque, a sticky film that constantly forms on your teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become inflamed, often appearing red, swollen, and tender. Gingivitis is reversible with proper oral hygiene. However, if left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form characterized by irreversible bone loss and potential tooth loss. Is periodontal disease contagious?
The bacteria responsible for triggering the inflammatory response in periodontal disease can be spread through saliva exchange. This transmission occurs most commonly through close contact activities such as:
- Kissing: While the risk is generally low for healthy individuals, kissing can facilitate the transfer of saliva and bacteria.
- Sharing Utensils: Eating with the same fork, spoon, or other utensil as someone with periodontal disease can introduce their bacteria into your mouth.
- Sharing Oral Hygiene Items: This is a significant risk factor. Sharing toothbrushes, floss, or other oral hygiene tools provides a direct pathway for bacteria to spread.
- Living in Close Quarters: Even sharing a glass or living in the same household as someone with periodontal disease can slightly increase your risk of bacterial transmission due to more frequent close contact.
It’s important to understand that the presence of these bacteria in your mouth doesn’t guarantee you’ll develop periodontal disease. Our bodies have defense mechanisms to combat harmful bacteria. However, certain factors can increase your susceptibility:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Insufficient brushing and flossing create a breeding ground for harmful bacteria, promoting plaque buildup and inflammation. As Dr. Ilya Aleksandrovskiy, M.D., MBA, notes, “It’s typically caused by poor brushing and flossing habits that allow plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to build up on the teeth and harden. In advanced stages, periodontal disease can lead to sore, bleeding gums; painful chewing problems; and even tooth loss.”
- Genetics: Some individuals are genetically predisposed to gum disease, making them more vulnerable even with good oral hygiene.
- Smoking: Smoking weakens the immune system and compromises the body’s ability to fight infection, significantly increasing the risk of periodontal disease.
- Medical Conditions: Certain systemic diseases like diabetes can increase susceptibility to infections, including periodontal disease.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as during pregnancy, can make gums more sensitive and vulnerable to inflammation.
Protecting Your Oral Health: Prevention and Treatment
Preventing the spread of periodontal disease-causing bacteria and reducing your risk of developing the disease hinges on maintaining excellent oral hygiene:
- Brush Thoroughly: Brush your teeth for two minutes, twice a day, using fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss Daily: Flossing removes plaque and food particles from between teeth and under the gumline, where your toothbrush can’t reach.
- Use Antimicrobial Mouthwash: Rinsing with an antimicrobial mouthwash can help further reduce bacteria in your mouth.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Professional cleanings and examinations are crucial for removing plaque and tartar buildup and detecting early signs of gum disease. Your dentist can also provide personalized advice and treatment recommendations.
- Avoid Sharing Oral Hygiene Items: This should go without saying, but sharing toothbrushes or any other oral hygiene tools is a significant risk and should be avoided at all costs.
If you notice any symptoms of gum disease, such as red, swollen, or bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, or loose teeth, seek dental care promptly. Early detection and treatment are essential to prevent further damage and potential tooth loss. Treatment options range from professional cleaning and scaling to more advanced procedures like root planing and surgery.
The Link Between Oral Health and Overall Health
Research increasingly suggests a link between periodontal disease and other health problems, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. While the exact mechanisms are still being investigated, inflammation associated with gum disease is thought to play a role. This connection underscores the importance of taking care of your oral health as part of your overall well-being. Is physical therapy covered by insurance?
Kissing and Periodontal Disease: Managing Risk
While a quick peck probably poses minimal risk, it’s prudent to be mindful, especially if your partner has advanced periodontal disease. Encourage them to seek treatment, and maintain your own excellent oral hygiene practices. Open communication about oral health concerns is also essential in any relationship.
Ongoing Research and Evolving Understanding
Research into the oral microbiome, the complex community of bacteria in our mouths, is ongoing. Scientists are learning more about the interactions between different bacteria, our immune systems, and our overall health. This evolving understanding may lead to more effective prevention and treatment strategies in the future. Staying informed and consulting your dentist for personalized advice are crucial steps in protecting your oral health.
- Delicious Meal Prep Cold Meals Ready to Grab and Go - March 10, 2026
- Cold Meal Prep Makes Healthy, Stress-Free Lunches Easy - March 9, 2026
- Meal Prep Ideas for Healthy Eating Throughout Your Busy Week - March 8, 2026