This guide provides comprehensive information about gum overgrowth, also known as gingival hyperplasia. We’ll explore the causes, symptoms, treatments, and prevention strategies to help you understand and manage this condition.
What is Gum Overgrowth?
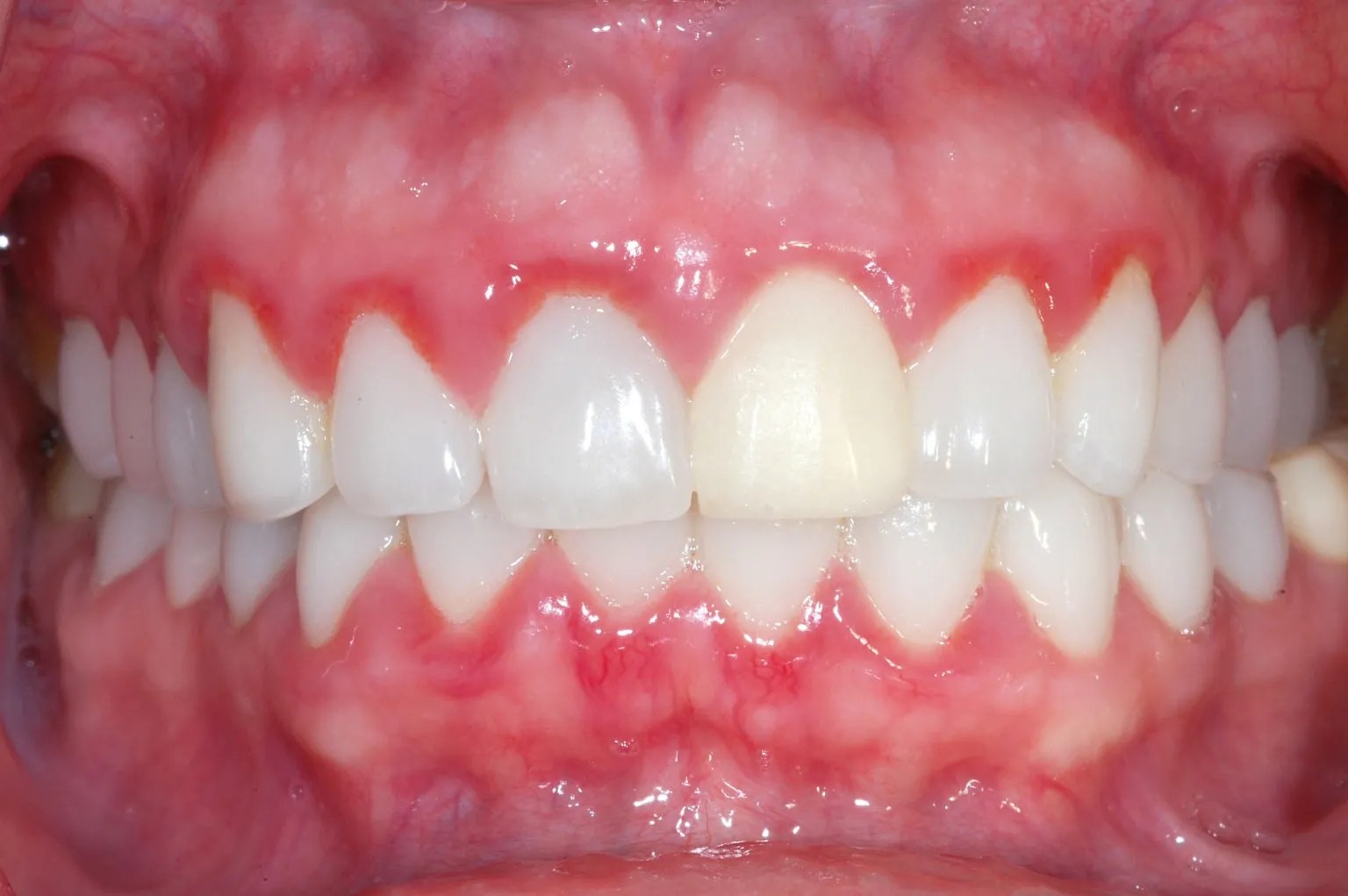
If you’ve noticed your gums creeping over your teeth, you might be experiencing gingival hyperplasia. This condition involves an excessive growth of gum tissue, which can partially or fully cover the teeth. It’s not merely a cosmetic issue; untreated gingival hyperplasia can negatively impact oral health, affecting tooth alignment and increasing the risk of gum disease. [https://chaztin.com/exposed-nerve-in-tooth]
Decoding the Causes
Several factors can contribute to gum overgrowth. Understanding the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment.
Poor Oral Hygiene
One of the most common culprits is inadequate oral hygiene. Plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, accumulates on teeth and along the gum line. If not removed through regular brushing and flossing, plaque hardens into tartar, further irritating the gums. This irritation can trigger inflammation and swelling, leading to gum overgrowth.
Medication Side Effects
Certain medications can unexpectedly stimulate gum growth. These include some anticonvulsants (used to treat seizures), immunosuppressants (used to prevent organ rejection), and calcium channel blockers (used to treat high blood pressure). While this side effect isn’t universal, it’s a possibility to be aware of. If you are taking these medications, maintain meticulous oral hygiene and discuss any gum changes with your doctor and dentist. They might be able to adjust your dosage or explore alternative medications. [https://chaztin.com/face-pull-alternatives]
Underlying Health Conditions
Sometimes, gum overgrowth can be a symptom of an underlying health issue. Leukemia, lymphoma, certain genetic disorders, hormonal imbalances, vitamin C deficiency (scurvy), and diabetes can contribute to gum overgrowth. Therefore, consistent medical care is vital.
Hormonal Shifts
Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy and puberty can also influence gum health. These changes can make gums more susceptible to inflammation and overgrowth.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Knowing the telltale signs of gum overgrowth allows for early detection and intervention.
Visual Cues
- Swollen, Puffy Gums: Gums appear enlarged and may even bulge.
- Red or Dark-Red Gums: A noticeable color change from the typical pale pink of healthy gums.
- Visible Overgrowth: Gum tissue partially or fully covers the teeth.
Physical Sensations
- Bleeding Gums: Gums bleed easily, especially during brushing or flossing.
- Tender or Painful Gums: Discomfort or pain when touching the gums.
Other Indicators
- Bad Breath (Halitosis): A persistent unpleasant odor.
- Difficulty Chewing or Speaking: Excess gum tissue can interfere with normal oral function.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the overgrowth and the underlying cause.
Non-Surgical Interventions
- Improved Oral Hygiene: The cornerstone of treatment. Diligent brushing, flossing, and regular professional cleanings are essential for removing plaque and tartar, reducing inflammation, and preventing further overgrowth.
- Medication Review: If medications are the likely culprit, consult your doctor about potential adjustments or alternatives. Never discontinue or alter medication without medical guidance.
Surgical Options
For more severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary.
- Gingivectomy: Surgical removal of excess gum tissue.
- Gingivoplasty: Reshaping of the gums to improve their contour and appearance.
- Laser Treatment: A less invasive alternative to traditional surgery, using lasers to remove excess gum tissue. This method often results in less bleeding and a faster recovery time.
Prevention Strategies
Proactive steps can significantly reduce your risk of developing gum overgrowth.
- Maintain Excellent Oral Hygiene: Brush twice daily, floss daily, and use an antimicrobial mouthwash as recommended by your dentist.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Schedule dental visits every six months for professional cleanings and checkups. Early detection of any gum issues can prevent them from escalating.
- Manage Underlying Conditions: If you have a health condition that could contribute to gum overgrowth, work closely with your doctor to manage it effectively.
Ongoing Research and Uncertainties
While much is known about gingival hyperplasia, research continues to explore the complexities of this condition. Scientists are investigating the influence of genetics, the link between gum disease and systemic health, and the development of new, less invasive treatments. Some experts suggest that specific genetic factors could play a more substantial role than currently understood. There’s also ongoing research into the efficacy of topical medications for gum overgrowth.
The Importance of Professional Guidance
This information is intended for educational purposes and does not replace professional medical advice. If you’re concerned about your gums, consult your dentist or doctor for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. They can assess your situation, determine the underlying cause, and recommend the most appropriate course of action. Remember, your oral health is a vital part of your overall well-being.
- Food Making Kits Bring Easy, Fun Homemade Dishes to Your Kitchen - February 5, 2026
- Cooking Kits Make Mastering New Recipes Fun for Everyone - February 4, 2026
- Leak-Proof Glass Food Containers with Locking Lids Keep Food Fresh - February 3, 2026