Navigating your dog’s skin issues can be challenging. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of Gentacalm, a commonly prescribed medication for canine skin conditions. We’ll delve into its uses, application, potential side effects, and important precautions to help you make informed decisions about your furry friend’s skin health.
Understanding Gentacalm: A Two-Pronged Approach to Skin Health
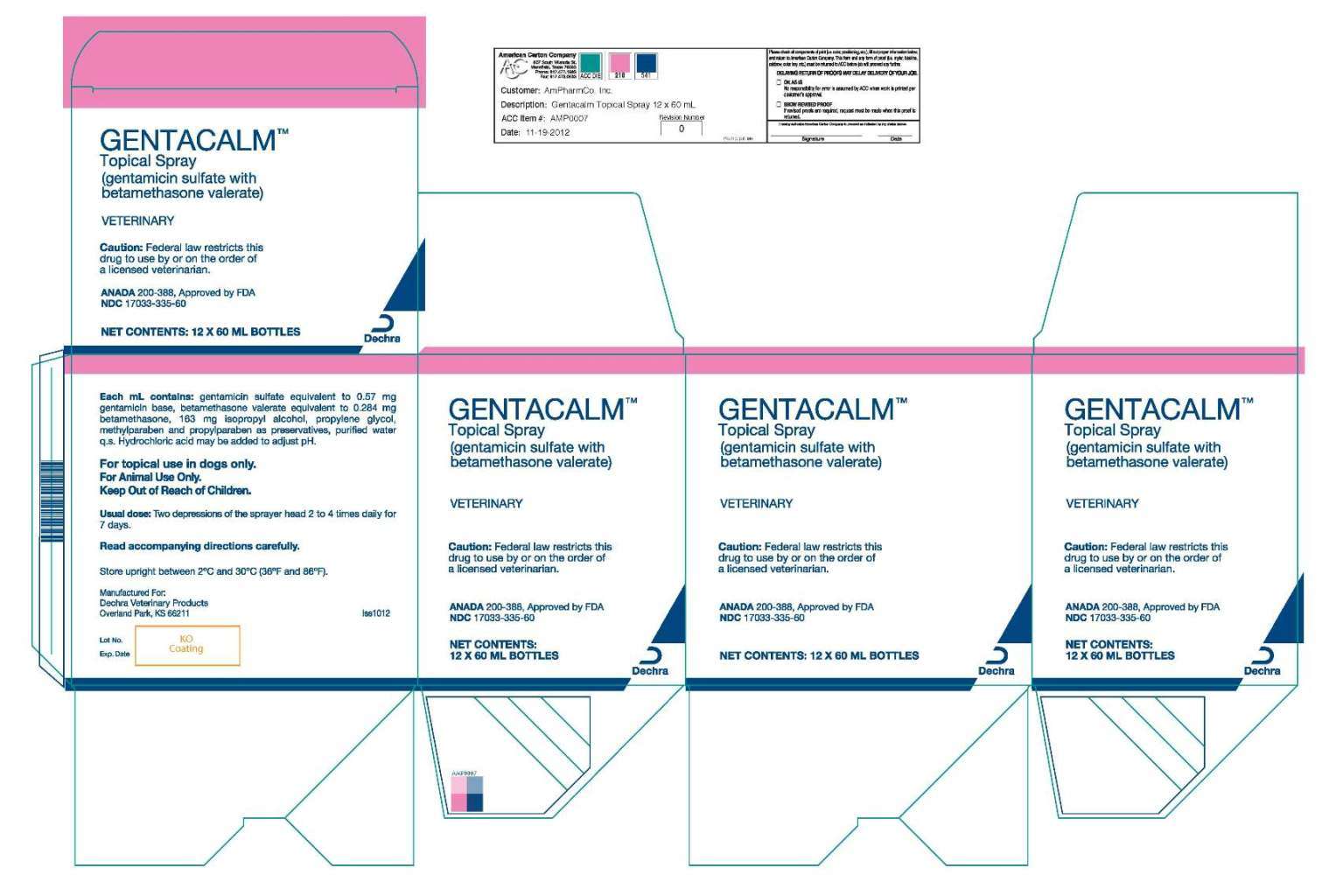
Gentacalm is a topical spray combining two active ingredients: gentamicin sulfate, an antibiotic, and betamethasone valerate, a corticosteroid. This dual-action formula targets both bacterial infections and inflammation, making it particularly effective for conditions like hot spots. Gentamicin combats bacterial growth, while betamethasone reduces inflammation, swelling, redness, and itching. This combination provides much-needed relief and promotes healing. You’ll need a prescription from your veterinarian to obtain Gentacalm, which is available in various sizes to suit your dog’s needs.
What Does Gentacalm Treat?
Gentacalm primarily targets infected superficial skin lesions in dogs. This includes:
- Hot Spots (Acute Moist Dermatitis): These inflamed, often oozing sores can appear suddenly and cause significant discomfort. Gentacalm is often a first-line treatment for hot spots due to its ability to quickly address both infection and inflammation.
- Superficial Pyoderma: Gentacalm is effective against bacterial skin infections, especially those caused by Staphylococcus and Pseudomonas bacteria.
- Post-Surgical Skin Infection Prevention: In some cases, veterinarians may prescribe Gentacalm to prevent infections in surgical sites.
It’s essential to remember that Gentacalm isn’t a cure-all for every skin issue. It specifically targets bacterial infections. If your dog’s skin problems stem from allergies, fungal infections, parasites, or other causes, Gentacalm may not be the appropriate treatment. A proper diagnosis from your veterinarian is crucial to determine the underlying cause and ensure effective treatment. They may also recommend the Skintegrity line for specific skin conditions. For conditions such as eczema, dermatitis, or psoriasis, Gentaved topical spray may be an option.
Gentacalm: Key Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Topical spray |
| Use | Treats infected superficial skin lesions (e.g., hot spots, pyoderma) |
| Active Ingredients | Gentamicin sulfate (antibiotic), Betamethasone valerate (anti-inflammatory) |
| Administration | Applied directly to the affected skin as directed by your veterinarian |
| Prescription | Required |
Applying Gentacalm Correctly
Proper application is crucial for Gentacalm’s effectiveness and to minimize potential side effects. Follow these steps:
- Preparation: Clean the affected area with a mild cleanser and clip away any excess hair. This allows the medication to reach the skin directly and prevents matting.
- Shaking: Shake the bottle well before each use to ensure even distribution of the active ingredients.
- Application: Hold the bottle 3-6 inches from the skin and spray the affected area. Each spray delivers a precise dose (0.7 mL), facilitating accurate administration. Typically, two sprays are sufficient per application.
- Frequency: Your veterinarian will likely recommend applying Gentacalm 2-4 times daily for about a week. Strictly adhere to their instructions, as the dosage and frequency may vary based on your dog’s specific condition and needs.
- Post-Application: Prevent your dog from licking the treated area for at least 10-15 minutes to allow the medication to absorb. An Elizabethan collar (cone) can be helpful.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
While Gentacalm is generally safe, some dogs may experience side effects. These are typically mild and may include:
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Vomiting or diarrhea may occur.
- Cushing’s Syndrome: Prolonged or excessive use can potentially lead to Cushing’s syndrome, a hormonal disorder.
- Delayed Wound Healing: Using Gentacalm for longer than the recommended duration can hinder the healing process.
Safety Precautions
- Strictly adhere to your veterinarian’s instructions.
- Limit treatment duration to 7 days unless otherwise directed.
- Monitor your dog closely for any unusual signs, especially during prolonged treatment.
- Prevent ingestion. If your dog licks the treated area excessively, consult your veterinarian.
- Do not use Gentacalm on cats. It can have severe adverse effects on felines.
Is Licking Gentacalm Dangerous?
While a small amount of licking is probably not cause for immediate alarm, excessive ingestion can lead to more pronounced side effects. Large amounts of ingested Gentacalm can contribute to:
- Gastrointestinal upset: Vomiting, diarrhea, sometimes with blood
- Liver, Adrenal, and Kidney Changes: Although rare, there is a possibility of histological changes in these organs.
- Lethargy: Listlessness and lack of energy can indicate systemic effects from ingestion.
If your dog ingests a significant amount of Gentacalm, consult your veterinarian immediately. They may recommend monitoring or supportive care based on your dog’s individual health. While there is no specific antidote, prompt veterinary consultation can help manage potential side effects.
To prevent licking, consider using an Elizabethan collar or closely supervise your dog after application. Keeping the treated area clean and dry may also reduce the temptation to lick. Some experts suggest that even small amounts of licking should be avoided, while others believe a minimal amount is tolerable. This discrepancy emphasizes the importance of individualized guidance from your veterinarian.
Ongoing Research and Alternatives
Current research continues to explore the long-term effects of Gentacalm, particularly with repeated use. While it remains a widely accepted treatment, consult your veterinarian about the latest research and potential alternatives. Some alternatives for bacterial skin infections include:
- Mupirocin or Fusidic Acid: These are topical antibiotics that may be suitable in some cases.
- Oral Antibiotics: For deeper or more severe infections, oral antibiotics might be necessary.
- Anti-inflammatory Medications (NSAIDs): These can help manage pain and inflammation associated with hot spots.
Conclusion
Gentacalm can be a highly effective tool for managing your dog’s skin conditions, offering relief and accelerating healing. By understanding its proper use, potential side effects, and precautions, you can contribute to your dog’s comfort and well-being. Remember, this guide is not a substitute for professional veterinary advice. Always consult your veterinarian for personalized recommendations and to address any specific concerns about your dog’s health. They can accurately diagnose the issue, determine if Gentacalm is suitable, and guide you on its safe and effective use.
- Meal Prep Ideas for College Students for Easy, Healthy Meals - March 12, 2026
- Easy Cold Meal Prep Ideas for No-Microwave Lunches on the Go - March 11, 2026
- Delicious Meal Prep Cold Meals Ready to Grab and Go - March 10, 2026