UTIs are notorious for their uncomfortable symptoms, but bloating is a lesser-known side effect that can add to the misery. This article explores the connection between UTIs and bloating, explaining the causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies.
Why UTIs Can Cause Bloating: Exploring the Connection
Experiencing a puffy, uncomfortable feeling in your lower abdomen along with the usual UTI symptoms? This bloating can stem from several factors related to the infection. UTIs primarily cause inflammation in the bladder and surrounding tissues. This swelling can create pressure and a feeling of fullness, similar to an overinflated balloon. Additionally, some bacteria, like the common culprit E. coli, produce gas during a UTI, further contributing to bloating. [https://chaztin.com/wrist-splint-for-tendonitis]
Another contributing factor is bladder function. A UTI can sometimes impair the bladder’s ability to empty completely. This retained urine adds to the pressure and discomfort, exacerbating the bloated feeling. It’s important to note that not everyone with a UTI experiences bloating, and the severity can vary.
Recognizing UTI Bloating: Identifying the Signs
While bloating isn’t a hallmark UTI symptom, it’s certainly possible. Recognizing UTI-related bloating involves considering both classic UTI symptoms and the specific nature of the bloating. The typical UTI symptoms include:
- Frequent Urination: A persistent urge to pee, even with little output.
- Burning Sensation: Pain or burning during urination.
- Cloudy or Smelly Urine: Changes in urine appearance and odor.
- Pelvic Pain: Discomfort or pain in the lower belly.
UTI-related bloating is typically localized in the lower abdomen, characterized by a feeling of fullness or pressure, sometimes accompanied by gas. If you’re experiencing these symptoms along with bloating, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. [https://chaztin.com/varicose-veins-before-and-after]
Managing UTI Bloating: Effective Strategies for Relief
Managing UTI bloating involves addressing the infection and alleviating the discomfort. Antibiotics are the cornerstone of UTI treatment, targeting the bacteria causing the infection. While antibiotics work, several strategies can help manage the bloating:
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out bacteria, reducing bladder irritation. It may seem counterintuitive when you feel bloated, but hydration is crucial for recovery.
- Heat Therapy: Applying a warm compress to the lower abdomen can soothe discomfort and potentially reduce inflammation.
- Dietary Adjustments: Avoiding gas-producing foods and incorporating probiotics may help alleviate bloating and support gut health. This is an area of ongoing research, and consulting a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized advice is recommended.
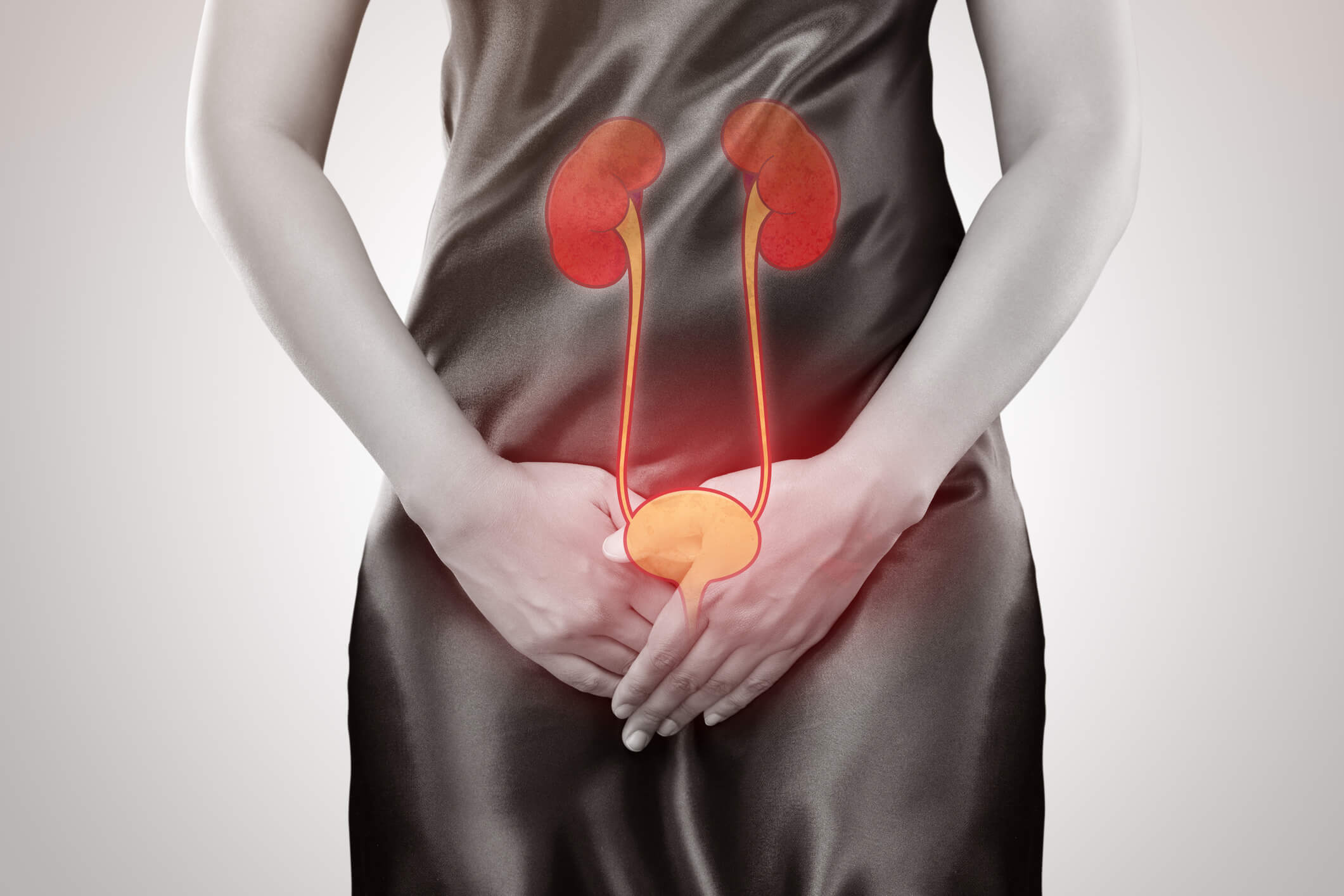
Kidney Involvement: Recognizing When a UTI Spreads
While UTIs typically affect the bladder and urethra, they can sometimes ascend to the kidneys, a condition known as pyelonephritis. Recognizing the signs of kidney involvement is crucial for prompt treatment:
- Back Pain: Usually focused around your flank (the side of your body between your ribs and hips), the pain can range from a dull ache to sharp and intense.
- Fever: Often accompanied by chills, fever is a common sign of a more serious infection.
- Chills: Intense shivering, even when warm.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms can further add to the discomfort.
These symptoms, combined with existing UTI discomfort, particularly back pain, fever, and chills, strongly suggest a possible kidney infection. Prompt medical attention is crucial to prevent complications like sepsis or kidney damage.
Ongoing Research and Considerations
Research into UTIs and their various manifestations is ongoing. Scientists are constantly learning more about the bacteria involved, the impact on the gut microbiome, and the effectiveness of different management strategies. Some studies suggest a link between gut health and UTI susceptibility, and research is exploring the role of probiotics and prebiotics in prevention and treatment.
It’s important to remember that medical advice can evolve. Staying informed and consulting with healthcare professionals is always recommended. They can provide the most up-to-date information and personalized advice based on your individual situation.
People’s Statements (verbatim):
- Dr. Himanshu J. Vats (MBBS, 1.5 years exp): “Yes, a urinary tract infection (UTI) can cause bloating in the stomach. There are a few reasons for this: Inflammation, Gas, Pressure…”
- Dr. Sumit Kapoor (MBBS, 9 years exp): “Several factors may cause frequent urination…Bloating is due to gastritis or improper food digestion.” (Note: This statement refers to bloating in general, not specifically UTI-related bloating).