Converting 101°C to Fahrenheit: Quick Answer and In-Depth Explanation
101°C is equal to 213.8°F.
Here’s the calculation: °F = (°C * 9/5) + 32. Therefore, (101 * 9/5) + 32 = 181.8 + 32 = 213.8°F.
Understanding the Celsius and Fahrenheit Scales
Celsius (also known as centigrade) and Fahrenheit are two different scales for measuring temperature. Celsius sets the freezing point of water at 0°C and the boiling point at 100°C. Fahrenheit sets freezing at 32°F and boiling at 212°F. These different scales arose from different historical approaches to defining temperature.
Visualizing the Conversion
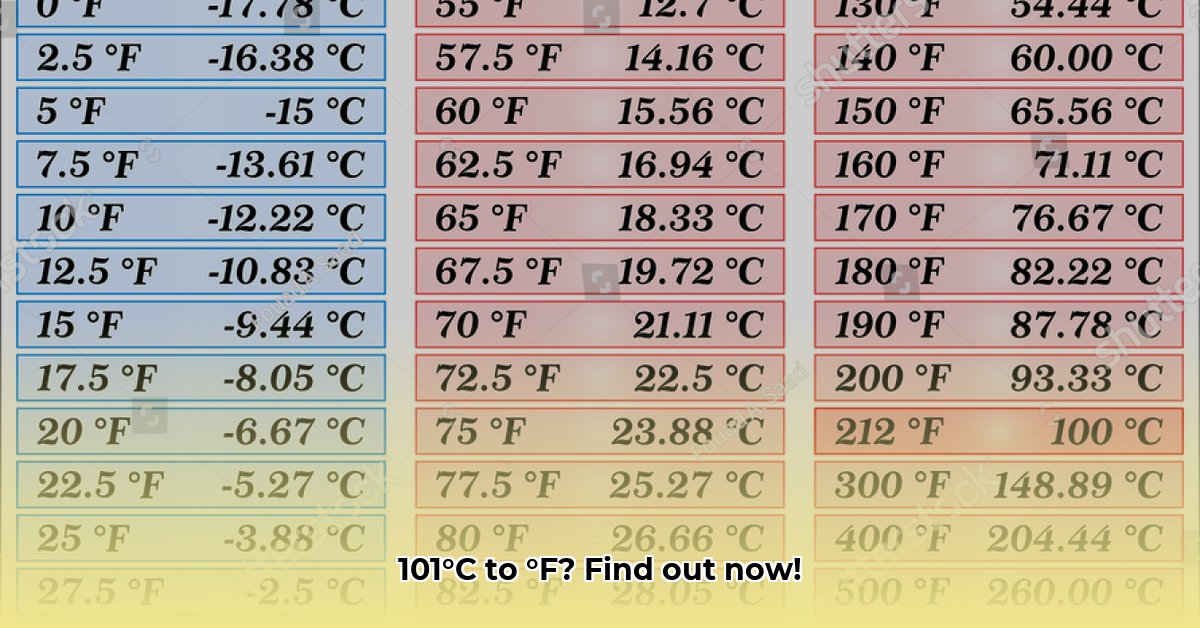
Here’s a conversion chart for temperatures around 101°C:
| Celsius (°C) | Fahrenheit (°F) |
|---|---|
| 99 | 210.2 |
| 100 | 212 |
| 101 | 213.8 |
| 102 | 215.6 |
| 103 | 217.4 |
A side-by-side visual representation of the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales would further enhance understanding (imagine two thermometers side-by-side, marked with both scales). 101°C would sit just slightly above the boiling point of water on the Celsius scale, corresponding to 213.8°F on the Fahrenheit scale.
Real-World Context and Applications
A temperature of 101°C (213.8°F) is slightly above the boiling point of water at standard atmospheric pressure. While not commonly encountered in everyday life, this temperature might be relevant in certain cooking scenarios (like candy making), industrial processes requiring specific temperatures, or in scientific research.
It’s also important to note that the boiling point of water can vary with changes in atmospheric pressure. At higher altitudes, water boils at a lower temperature, so 101°C might be closer to boiling in such environments.
Here are some common temperature conversions for context:
- Body temperature: 37°C = 98.6°F
- Room temperature: 20°C = 68°F
- Boiling point of water (at sea level): 100°C = 212°F
Deeper Dive into Temperature Scales
The Celsius scale, being part of the metric system, is widely adopted for scientific and everyday use globally. Its basis on the properties of water makes it intuitive. Fahrenheit, however, is more prevalent in the United States. Its history is less straightforward, with its zero point likely derived from a very cold winter Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit observed. Fahrenheit’s scale, with its smaller degrees, allows for greater precision in expressing everyday temperature variations.
Quick Estimation Techniques and Further Exploration
For a quick, rough estimate when converting from Celsius to Fahrenheit, you can double the Celsius value and add 30. So, for 101°C, this would be (101 * 2) + 30 = 232°F. This approximation is useful for quick mental calculations but isn’t precise enough for situations requiring accuracy, such as cooking or scientific applications.
Online resources provide calculators and conversion charts for precise conversions between Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin (another temperature scale used primarily in scientific contexts).
While the standard formula provides precise conversions, factors like thermometer calibration and measurement methods may introduce slight variations. These are typically negligible in everyday situations but can be important in scientific research where high precision is crucial.
Ongoing research in areas like thermodynamics, material science (particularly at extreme temperatures), and metrology (the science of measurement) continues to refine our understanding of temperature and its measurement. This ongoing exploration may lead to further evolution in our understanding and the development of even more precise temperature measurement tools.
- Glass Storage Bowls With Glass Lids Offer Superior Freshness - January 28, 2026
- Rectangular Glass Food Storage Containers For Meal Prep - January 27, 2026
- Borosilicate Glass Food Containers Keep Meals Fresh and Organized - January 26, 2026