This comprehensive guide explores the causes, treatments, and preventative measures for Botox-induced eyelid droop, providing you with the knowledge to approach this cosmetic procedure with confidence.
Understanding Eyelid Droop After Botox
Sometimes, after a Botox injection, you might experience a temporary drooping of the eyelid. This is formally known as ptosis. While a bit unnerving, it’s usually temporary and treatable. This section explains the causes, symptoms, and what you can do about it.
What Causes Eyelid Droop?
Botox works by relaxing muscles. Occasionally, the Botox may unintentionally affect the levator palpebrae superioris muscle, responsible for lifting your eyelid. This likely happens when the Botox migrates slightly from the intended injection site. Factors such as individual facial anatomy and the precise placement of the injections can influence this migration.
Recognizing the Symptoms
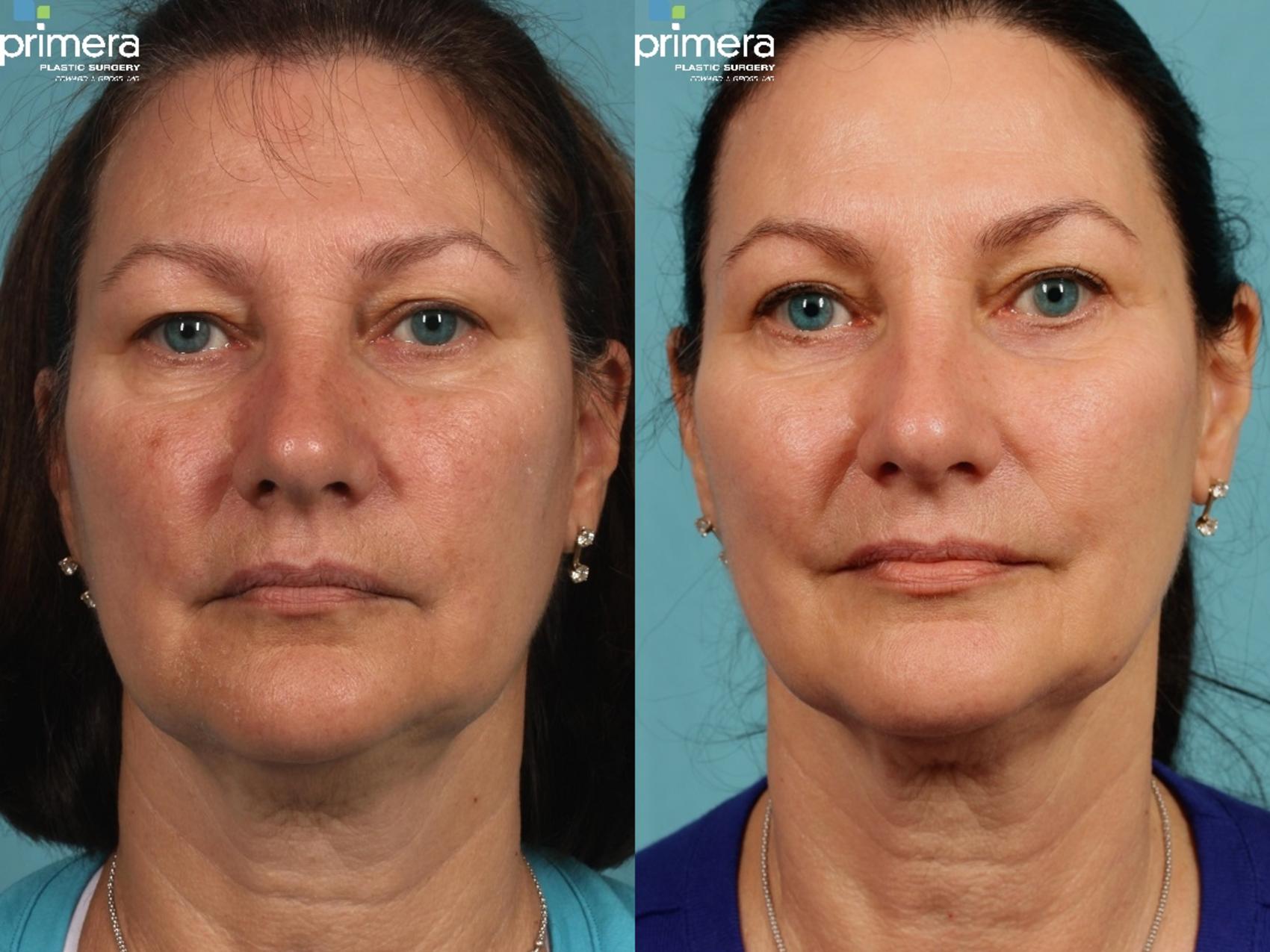
Eyelid droop can range from subtle to more noticeable. You might feel a heaviness in your eyelid or have difficulty opening it fully. It can sometimes obstruct vision, similar to a curtain partially drawn over your eye. The severity varies from person to person. See before and after results to better understand the potential impact. For a personalized cost estimate, reach out for UPNEEQ cost information.
Treating and Preventing Eyelid Droop
Fortunately, several treatment options can manage and even reverse eyelid droop.
Treatment Options
- Eye Drops (Apraclonidine): These drops stimulate Müller’s muscle, which assists in lifting the eyelid. This is a non-invasive option often providing noticeable improvement.
- Eye Exercises: Targeted exercises can strengthen the levator muscle over time, gradually restoring the eyelid’s position. Consult your doctor for suitable exercises.
- Strategic Botox Injections: In some cases, strategically placed Botox injections in the brow can indirectly lift the eyelid.
- Surgery (Rarely Necessary): Surgery is generally a last resort for severe cases unresponsive to other treatments.
Preventing Eyelid Droop
The best preventative measure is choosing a qualified and experienced injector. Their expertise in facial anatomy and injection techniques significantly reduces the risk of complications like ptosis. Don’t hesitate to inquire about their experience and training.
Patient Perspectives and Ongoing Research
Real patient experiences can offer valuable insights. “I noticed my left eyelid drooping a few days after my Botox injections. It wasn’t painful, but it was noticeable and bothersome. My doctor prescribed eye drops, which helped within a few weeks,” shares Patient A.
Research into eyelid ptosis and its management is ongoing, suggesting that even more effective treatments may emerge in the future.
Does Botox Eyelid Droop Go Away?
Yes, in most cases, Botox-induced eyelid droop is temporary and resolves as the Botox wears off, typically within 4-8 weeks. This section delves deeper into the reasons, recovery process, and management strategies.
Why Does it Happen and How Long Does it Last?
The droop occurs when Botox inadvertently affects the levator palpebrae superioris muscle. This is relatively rare, affecting less than 1% of Botox recipients. The effects typically subside within 4-8 weeks, but can sometimes resolve faster, even within a month. Botox administered to the forehead however, can last considerably longer, typically 3-4 months.
Managing the Droop
Several strategies can help manage a droopy eyelid:
- Warm Compresses: These may stimulate blood flow, potentially aiding recovery.
- Eyelid Tape: This provides a temporary cosmetic lift.
- Prescription Eye Drops (e.g., Apraclonidine): Consult a doctor, as these can have side effects.
Preventing Future Occurrences
Choosing a qualified injector proficient in facial anatomy and injection techniques is paramount for preventing complications.
Why Are My Eyes More Hooded After Botox?
Botox can sometimes make eyelids appear more hooded. This section explores the reasons and solutions.
Understanding the Cause
This probably results from how Botox affects the forehead muscles. When these muscles relax, the eyebrows may subtly droop, causing excess skin to fold over the eyelids, creating a hooded appearance. It’s like a pulley system; if the brow descends, the eyelid skin follows. Another less common possibility is Botox migrating to the levator palpebrae superioris, causing ptosis.
Factors Influencing Hooded Eyelids
- Pre-existing Muscle Weakness: Botox can exacerbate naturally weak forehead muscles, making the drooping more prominent.
- Injection Placement and Dosage: Injecting too much Botox, or injecting it too close to the eyebrow, increases the risk of drooping.
- Individual Anatomy: Some individuals are simply more susceptible due to their unique facial structure.
Managing and Minimizing the Effect
The Botox’s effects are temporary, usually lasting three to four months. If the hooding is bothersome, consider the following:
- Eye Drops (e.g., Apraclonidine or Brimonidine): These can temporarily stimulate the muscles that lift the eyelid. Consult your doctor first.
- Additional Botox (Strategically Placed by an Experienced Doctor): Can potentially counteract the droop.
- Surgery (Long-Term Solution): Blepharoplasty (eyelid surgery) is considered a more permanent solution.
Prevention involves selecting a skilled injector and discussing placement and dosage beforehand.
Where Not to Inject Botox for Droopy Eyelids?
This section highlights the areas around the eyes where Botox injections should be avoided to minimize the risk of droopy eyelids.
Avoiding the Danger Zones
To prevent Botox from affecting the levator palpebrae superioris muscle, avoid these areas:
- Eyelid Margin: Maintain a safety zone of at least one to two centimeters away from the eyelid edge.
- Medial Brow: Exercise extreme caution in this area between the eyebrows, as it’s close to the levator muscle.
- Upper Eyelid: Never inject Botox directly into the upper eyelid due to the high risk of complications.
Understanding the Mechanisms and Managing the Risk
Several theories exist regarding how Botox causes ptosis. Some believe it’s purely migration, while others suggest more complex interactions. Further research is ongoing. Even with precautions, some drooping can occur. This is usually temporary and resolves within a few weeks (typically 4-8). Manage it with warm compresses, eyelid tape, or specific eye drops under a doctor’s supervision.
The Importance of an Experienced Injector
Choosing a skilled injector with a deep understanding of facial anatomy is critical. They can tailor the treatment and minimize risks.
Key Points:
- Definition and Causes: Eyelid droop (ptosis) occurs when Botox migrates to the levator muscle.
- Appearance and Symptoms: Drooping eyelids, potentially affecting vision.
- Treatment: Eye drops, exercises, strategic Botox, and rarely surgery.
- Prevention: Choosing a qualified injector.
This information is for general knowledge and does not constitute medical advice. Consult a healthcare professional for any concerns after receiving Botox.
- Healthy Food Near Me That Delivers Warm, Fresh, Ayurvedic Indian Tiffins - January 7, 2026
- Low Sodium Meal Plans Delivered Make Healthy Eating Easy - January 6, 2026
- Find Low Sodium Meal Prep Delivery For Heart Health - January 5, 2026